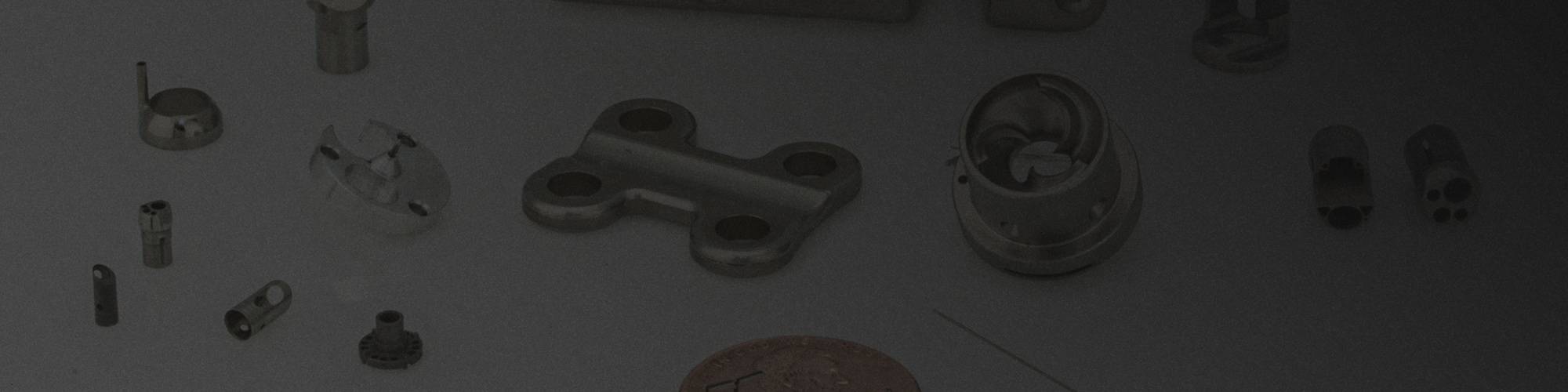
Micromachining
CNC Micromachining of Complex Small Components
The demand for micromachining services is growing worldwide. Advancements in the medical, fiber optic, and satellite industries require micromachining companies to improve their precision capabilities. If you’re looking for a company that understands this and is ahead of the curve, Owens Industries is the right place.
Owens is ahead of the industry trend, offering ultra-precision micromachining services to clients. While our sweet spot is in medium-sized components comparable in size to a volleyball, we will take on micromachining projects where strict tolerances are a priority. Have problem parts or impossible components? Call upon our expertise.
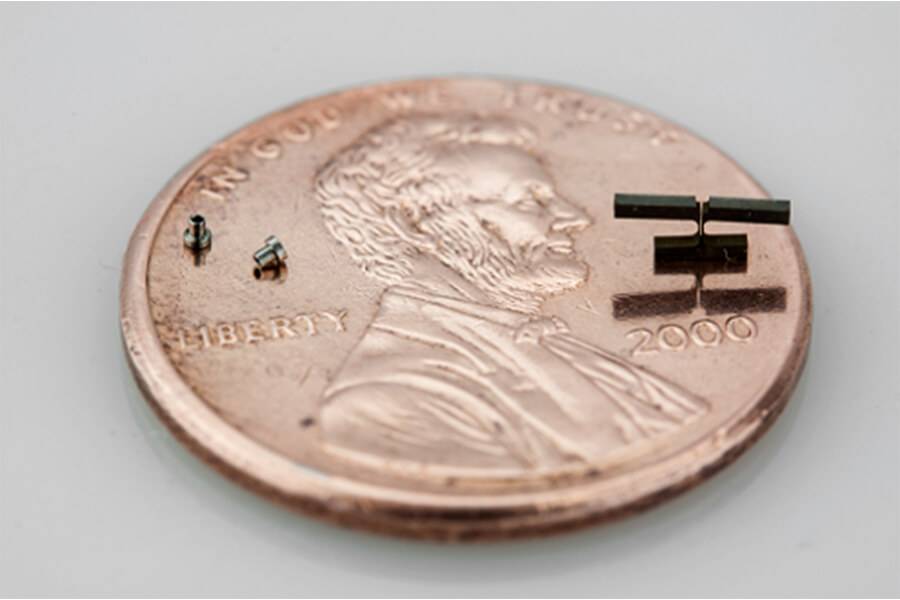
What is Micromachining?
Micromachining is a specialized machining process involving the production of small and intricate parts with high levels of accuracy and tolerance control. Micromachining typically involves using specialized tools, such as micro-drills and micro-lathes, to produce parts with dimensions in the micrometer range (less than 1 millimeter).
Precision micromachining is often used in the production of medical devices, aerospace components, and other critical components that require precise tolerances and high levels of detail. The process involves using advanced computer-controlled equipment to produce micro parts that meet strict design specifications. Precision micromachining requires skilled machinists and a thorough understanding of manufacturing processes and materials to ensure successful production.
Why Choose Owens Industries for Micromachining?
Owens Industries stands out as a premier choice for micromachining services, with unparalleled expertise, advanced capabilities, and a longstanding commitment to precision manufacturing. With over six decades of experience, Owens Industries’ machinists consistently demonstrate a mastery of the precision micromachining techniques required for intricate and small components. Our comprehensive suite of micromachining capabilities, including state-of-the-art EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) techniques such as Sink EDM and Wire EDM Cutting allow us to handle a diverse range of materials, from alloy steel and aluminum to brass, copper, and even specialized alloys like Hastelloy.
View our Success Gallery to see our work!
Benefits of Micromachining
These components can be cut down to one-thousandth of a millimeter, helping make the production of tiny parts more efficient and realistic. Also known as micro/mesoscale mechanical manufacturing (M4 processes), micromachining creates products one by one, helping to establish consistency with dimensions between parts. If you want access to predictable and controlled turnaround times and quality surface finishes, contact Owens Industries for more information regarding how micromachining can help save your company time and money.
Micro Precision Machining Using Sink EDM
Small and unusual shapes, such as gears or other micron parts requiring detailed intricacies, are best made using Sink EDM. During Sink EDM, complex shapes are formed through erosion, caused by a spark between the part being machined and the custom-designed electrode of the sinker EDM center.
Well-known Sinker EDM machined materials include:
- Stainless steel
- Aluminum
- Brass
- Copper
- Titanium
- Ferrous & Non-Ferrous Metals
Micromachining Using Wire EDM Cutting
We also offer EDM micromachining using state-of-the-art wire EDM machines. Our Wire EDM is capable of .001” diameter cutting wire, offering extremely fine EDM micromachining options. To achieve true micromachining with EDM, our EDM machines have 0.1-micron resolution glass scales.
Micro Milling Through 5 Axis Technology
Owens’ 5-axis micro-milling centers come from leading German manufacturers and are specially calibrated to achieve the highest precision results during micro-milling. We ensure all elements of our micromachining process are carefully calculated and executed for incredible product results, whether it be the fluids used in micro-cutting, controlling vibrations from micro-drilling or component handling. Regardless of the CNC machining processes required to make your micro part, Owens Industries has the solutions you need to make it happen.
Materials
Micromachining Materials Trusted by Owens Industries
Owens Industries excels in micromachining services with extensive experience in treating parts made from various materials.
- Brass
- Copper
- Stainless Steel
- Tool Steel
- Alloy Steel
- Aluminum
- Hastelloy
- Inconel
- Invar
- Maraging Steel
- Titanium

Brass
Brass is a metal known for its easy machinability and good electrical conductivity. It is ideal for applications requiring low friction, such as gears, locks, and musical instruments.
| Brass | UNS Designation | DIN Designation | Alternative Designation |
|---|---|---|---|
| C36000 | UNS C36000 | CUZN39PB3 | CuZn39Pb3 |
| C46400 | UNS C46400 | CuZn38Al | Naval Brass |
| C93200 | UNS C93200 | Saems 660 | Bearing Bronze |
| C48500 | UNS C48500 | CuZn39Sn1 | Leaded Muntz Metal |
| C26000 | UNS C26000 | CUZN30 | Cartridge Brass |
| C37700 | UNS C37700 | CUZN40PB2 | Forging Brass |

Copper
Copper is excellent at conducting heat and electricity, making it perfect for electrical uses like busbars and wire connectors. It is easily recognized by its shiny reddish-orange color and is also used in plumbing and roofing.
| Copper | UNS Designation | DIN Designation | Alternative Designation |
|---|---|---|---|
| C11000 | UNS C11000 | Cu-ETP | Electrolytic Tough Pitch (ETP) Copper |
| C10100 | UNS C10100 | OF-OK | Oxygen-Free Electronic (OFE) Copper |
| C10200 | UNS C10200 | OF-Cu | Oxygen-Free (OF) Copper |
| C28000 | UNS C28000 | CuZn40 | Muntz Metal |
| C14500 | UNS C14500 | TeCu | Tellurium Copper |

Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is known for its strength, heat, and corrosion resistance, along with its durability and attractive appearance. These qualities make it suitable for a wide range of uses, including kitchenware, medical instruments, and construction.
| Stainless Steel | UNS Designation | DIN Designation | Alternative Designation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 316L | UNS S31603 | X2CrNiMo17-12-2 | Stainless Steel 316L |
| 304 | UNS S30400 | X5CrNi18-10 | Stainless Steel 304 |
| 17-4 PH | UNS S17400 | X5CrNiCuNb16-4 | Stainless Steel 17-4 PH |
| 303 | UNS S30300 | X8CrNiS18-9 | Stainless Steel 303 |
| 420 | UNS S42000 | X20Cr13 | Stainless Steel 420 |
| 440C | UNS S44004 | X105CrMo17 | Stainless Steel 440C |

Tool Steel
Tool steels are hard, stiff, and resistant to abrasion, making them perfect for manufacturing industrial tools. Their robustness is essential for cutting, drilling, and molding applications in various industries.
| Tool Steel | UNS Designation | DIN Designation | Alternative Designation |
|---|---|---|---|
| D2 | UNS T30402 | 1.2379 | X155CrVMo12-1 |
| M2 | UNS T11302 | 1.3343 | HS6-5-2C |
| A2 | UNS T30102 | 1.2363 | X100CrMoV5-1 |
| S7 | UNS T41907 | 1.2355 | 50CrMoV13-15 |
| O1 | UNS T31501 | 1.2510 | 100MnCrW4 |
| H13 | UNS T20813 | 1.2344 | X40Cr |

Alloy Steel
Alloy steels include additional elements beyond carbon, which improve their hardness, toughness, and resistance to fatigue and wear. These steels are widely used in construction, automotive, and machinery due to their enhanced properties.
| Alloy Steel | UNS Designation | DIN Designation | ISO Designation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4140 | 1.7225 | 708M40 | 42CrMo4 |
| 4340 | 1.6565 | 817M40 | 40NiCrMo6 |
| 8620 | 1.6523 | 805M20 | 20NiCrMo2 |
| 52100 | 1.3505 | 100Cr6 | SUJ2 |
| 4142 | 1.7227 | 708M40T | 41CrMoS4 |
| 6150 | 1.8159 | 735A51 | 50CrV4 |

Aluminum
Aluminum alloys are lightweight and strong, with excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. They are also resistant to corrosion and can be anodized for added protection, making them ideal for aerospace and packaging industries.
| Aluminum Alloy | UNS Designation | DIN Designation | ISO Designation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7075-T651 | 3.4365 | 76528 | AlZn5.5MgCu |
| 6082-T651 | 3.2315 | 64430 | AlSi1MgMn |
| 6060 | 3.3206 | EN AW-6060 | AlMgSi |
| 5052 | EN AW-5052 | 3.3523 | AlMg2,5 |
| 2017A | 3.1325 | 24530 | AlCu4MgSi |

Hastelloy
Hastelloy is a group of nickel alloys known for their high resistance to corrosion, pitting, and stress-corrosion cracking. They are often used in harsh environments like chemical processing and aerospace, where durability is crucial.
| Hastelloy | UNS Designation | DIN Designation | Alternative Designation |
|---|---|---|---|
| C276 | UNS N10276 | 2.4819 | NiMo16Cr15W |
| C22 | UNS N06022 | 2.4602 | NiCr21Mo14W |
| B-2 | UNS N10665 | 2.4617 | NiMo28 |
| X | UNS N06002 | 2.4665 | NiCr22Fe18Mo |
| C2000 | UNS N06200 | 2.4675 | NiCr23Mo16Cu |
| G-30 | UNS N06030 | 2.4603 | NiCr29Mo9Fe |

Inconel
Inconel is a strong, corrosion-resistant nickel alloy, ideal for challenging aerospace applications. It can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for jet engines and gas turbines.
| Inconel | UNS Designation | DIN Designation | Alternative Designation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 718 | UNS N07718 | 2.4668 | NiCr19Fe19Nb5Mo3 |
| 625 | UNS N06625 | 2.4856 | NiCr22Mo9Nb |
| 600 | UNS N06600 | 2.4816 | NiCr15Fe |
| X-750 | UNS N07750 | 2.4669 | NiCr15Fe7TiAl |
| 601 | UNS N06601 | 2.4851 | NiCr23Fe |
| 725 | UNS N07725 | 2.4668 | NiCr19Fe19Nb5Mo3 |

Invar
Invar is a nickel alloy with very low thermal expansion, making it highly stable and perfect for precision applications such as instrumentation and aerostructure molds. It is also used in scientific instruments where dimensional stability is critical.
| Invar | UNS Designation | DIN Designation | Alternative Designation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 36 | UNS K93600 | 1.3912 | FeNi36 |
| 42 | UNS K94200 | 1.3917 | FeNi42 |
| 48 | UNS K94800 | 1.3922 | FeNi48 |
| 32-5 | UNS K94610 | 1.3911 | FeNi32-5 |
| 42-6 | UNS K94620 | 1.3913 | FeNi42-6 |
| 46 | UNS K94630 | 1.3914 | FeNi46 |

Maraging Steel
Maraging steels are ultra-high-strength steels that are easy to machine and weld without causing distortion. They gain their exceptional hardness and toughness from a special heat-treating process, making them suitable for aerospace and tooling applications.
| Maraging Steel | UNS Designation | DIN Designation | Alternative Designation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | UNS K93120 | 1.6359 | 20Ni Maraging Steel C200 |
| 250 | UNS K92890 | 1.6358 | 18Ni Maraging Steel C250 |
| 300 | UNS K93120 | 1.6354 | 18Ni Maraging Steel C300 |
| 350 | UNS K93160 | 1.6356 | 18Ni Maraging Steel C350 |
| 400 | UNS K91460 | 1.6352 | Custom 465 Stainless |
| 500 | UNS K92810 | 1.6354 | Custom Age 625 Plus |

Titanium
Titanium is a lightweight metal with excellent strength, low thermal expansion, and high corrosion resistance. Its ability to be sterilized and its biocompatibility make it unique, especially in medical implants and aerospace components.
| Titanium Grade | UNS Designation | DIN Designation | Alternative Designation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) | UNS R56400 | 3.7165 | Ti-6Al-4V |
| 2 | UNS R50400 | 3.7035 | CP Titanium |
| 23 (Ti-6Al-4V ELI) | UNS R56401 | 3.7165 | Ti-6Al-4V ELI |
| 9 (Ti-3Al-2.5V) | UNS R56320 | 3.7195 | Ti-3Al-2.5V |
| 7 (Ti-0.2Pd) | UNS R52400 | 3.7235 | Ti-0.2Pd |
| 12 (Ti-0.3Mo-0.8Ni) | UNS R53400 | 3.7105 | Ti-0.3Mo-0.8Ni |
Industries
Micro-Cut Components for Every Industry
Numerous industries are eagerly following the trend of utilizing miniature parts in their product applications. The extreme attention to detail, dedication to precision, and high level of expertise garnered in our employees is what sets us apart to serve these industries with precision micromachined components.


Complex Components We’ve Micromachined
- Miniature gears for the ophthalmic industry
- Sonic nozzles with precision venturis for flow measurement
- Miniature components for nuclear armament timing devices
- Components for respiration monitoring equipment
- Electron microscope accessories
- Fiber optic components including MEMs
- Optical switch components such as collimators
- Impellers for VAD – Ventricular Assist Devices: heart pumps
Contact Owens Industries for machining services including micromachining for your complex parts today.
FAQ
Micromachining Frequently Asked
Questions
What is micromachining?
Micromachining is a type of manufacturing process that involves the production of small and intricate parts with dimensions in the micrometer range (less than 1 millimeter). It typically involves the use of specialized tools, such as micro-drills and micro-lathes, to produce parts with high levels of precision and accuracy.
What is micromachining used for?
Micromachining is used for the production of small and intricate parts with dimensions in the micrometer range (less than 1 millimeter). It is often used in the production of medical devices, such as stents, catheters, and implantable devices, as well as aerospace components, such as sensors and fuel injectors. In addition, micromachining is also used in the production of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), which are tiny devices that combine mechanical and electronic elements on a microscale.
What is bulk micromachining?
Bulk micromachining is a type of manufacturing process that involves the removal of large volumes of material from a substrate to create microscale features or structures. It is often used in the production of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), which are tiny devices that combine mechanical and electronic elements on a microscale. Bulk micromachining is typically performed using a combination of photolithography and etching techniques, which allow for precise control over the shape and size of the features being created.
What is surface micromachining?
Surface micromachining is a type of manufacturing process that involves the creation of microscale features or structures on the surface of a substrate. It is often used in the production of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), which are tiny devices that combine mechanical and electronic elements on a microscale. Surface micromachining is typically performed using a combination of photolithography and etching techniques, which allow for precise control over the shape and size of the features being created.
What are the advantages of micromachining?
Some of the advantages of micromachining include enhanced accuracy, increased efficiency, improved functionality, increased durability, and added cost savings over other methods.